Cerebral Artery Occlusion Pathophysiology
The literature reports some 65 cases of MCA occlusion following non-penetrating blunt trauma to the head. 109 132 275 277 439 442 However in most patients with SCA strokes no arterial occlusion is found.
Anterior cerebral artery occlusion leads to contralateral hemiparesis affecting the leg more severely than the arm.
Cerebral artery occlusion pathophysiology. Arterial occlusions leading to strokes in the SCA distribution usually involve the distal tip of the BA the ICVA the ECVA at its origin and less frequently the SCA itself. Involving the shoulder more than the hand. Cause of cerebral ischemia. Caplan in Stroke Fourth Edition 2004 Causes. Both circulations are connected by the posterior communicating arteries PCOM which make up the circle of Willis. The most common causes of arterial occlusion involving the major cerebral arteries are 1 emboli most commonly arising from atherosclerotic arterial narrowing at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery from cardiac sources or from atheroma in the aortic arch and 2 a combination of atherosclerotic stenosis.
Presumably the thromboembolus has moved. A neversymptomatic ICA occlusion has a relatively benign course whereas symptomatic occlusion increases future risk of strokes. Large artery occlusion typically results from embolization of atherosclerotic debris originating from the common or internal carotid arteries or from a cardiac source. None has developed further ischemia after the initial stroke and 4. Although total carotid artery occlusion may be caused by different disease entities by far the most frequent cause remains atherosclerosis. Ncbinlmnihgov The most common presenting symptom of PCA dissection is occipital headache.
Chronic middle cerebral artery MCA occlusion as a cause of hemodynamic stroke has not been a prominent clinical issue in the Western world. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced by right unilateral common carotid artery occlusion causes delayed white matter lesions and cognitive impairment in adult mice. Atherosclerotic disease of the middle cerebral artery MCA is a relatively rare condition occurring in only 7 to 8 of patients presenting with stroke in the MCA distribution. Some lines of evidence have suggested that subcortical ischemic vascular dementia SIVD is a common form of vascular dementia VaD and that its pathological changes are the development of ischemic. The alternative MCAO model described here allows the reperfusion of the common carotid artery CCA and. 1 2 3 Subsequent MCA stenosis or occlusion may lead to transient ischemic attacks TIAs or frank stroke thus prompting the need for intervention.
The 40 patients were classified into three groups according to the site of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Capsular branch occlusion Heubner Artery clinical features Faciobrachial monoplegia which is proximal more than distal ie. We therefore tested whether fMCAO induces ischemiareperfusion damage in retina in mice. In hemorrhagic stroke a cerebral artery leaks blood which damages adjacent brain tissue. They are caused by occlusion of deep penetrating branches of major cerebral arteries and are particularly common in hypertension and diabetes which are associated with severe atherosclerosis of small vessels and small vessel disease see below. 1 In addition emboli especially those from the.
Up to 10 cash back Molecular and Systemic Pathophysiology. The middle cerebral artery occlusion MCAO model is clinically relevant and the most frequently used surgical model of ischemic stroke in rodents. The middle cerebral artery MCA is the most common artery involved in acute stroke. They occurred in areas of paracentral scotomas right in Patient 1 and left in Patient 2. While endovascular treatment is established for anterior circulation large vessel occlusion stroke little is known about the course of acute fetal posterior cerebral artery occlusions. A small lacunar infarct eg one involving the internal capsule can cause as severe a neurological deficit as can a.
Australia Abstract Traumatic occlusion of the middle cerebral artery MCA is a rare cause of cerebral infarct. The most common cause of MCA occlusion is embolism and sudden occlusion of the proximal MCA by an embolus is one of the most frequent causes of major stroke. Acute cerebral artery occlusion by an embolus or by local thrombosis is the most common but an etiopathophysiological heterogeneous cause of stroke. There were 13 patients with occlusion of the proximal portion of the Ml segment 13 with distal Ml segment. Cognitive changes resembling a global dementia may occur and be accompanied by incontinence. Causes of embolism ie cardiomyopathy valvular heart disease cardiac arrhythmia and carotid ulceration were excluded.
These vessels provide blood supply to parts of the frontal temporal and parietal lobes of the brain as well as deeper structures including the caudate internal capsule. Residual personality changes of a frontal type can occur. Anterior cerebral artery strokes occur in the territory of the anterior cerebral artery which involves the superior and medial part of the parietal lobe along with the midline of the frontal lobe. In ischemic stroke occlusion of a cerebral artery causes damage to the brain tissue dependent on blood supply from the affected vessel. The diagnosis and management of acute fetal posterior cerebral artery occlusion are challenging. We describe a case of MCA occlusion following blunt head trauma.
Generally etiology is differentiated into large vessel occlusion of the extra- and intracranial brain supplying arteries 40 small vessel. A grasp reflex and motor dysphasia may be present. When there is an occlusion in the cerebral vasculature the circle of Willis as well as collateral circulations provide blood to the occluded areas. A complete occlusion of the internal carotid artery ICA is an important cause of cerebrovascular disease. The proximity of the ophthalmic artery to the middle cerebral artery suggests that fMCAO induces retinal ischemia. These are uncommon causes of ischemic infarctions making up about 03-44 of stroke cases in series reports.
This article reviews the surgical and endovascular. Ultrasonography magnetic resonance imaging and contrast angiography are useful diagnostic tests and functional. SUMMARY Ten patients with angiographically verified occlusion of the basilar or vertebral artery have been followed for an average of 275 years. Occlusion of the Vertebral or Basilar Artery Follow Up Analysis of Some Patients with Benign Outcome Louis R. It branches directly from the internal carotid artery and consists of four main branches M1 M2 M3 and M4. However the outcomes of this model such as lesion volume are associated with high levels of variability particularly in mice.
Filamentous middle cerebral artery occlusion fMCAO is the most frequently used focal cerebral ischemia model in rodents. However because of uncertainty about the pathophysiology of symptomatic internal carotid artery ICA occlusion there has been contro-versy surrounding its proper management. Visual hallucinations were the presenting symptoms in 2 patients with probable infarcts in the territory of a posterior cerebral artery.

Collateral Recruitment After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Mca Download Scientific Diagram
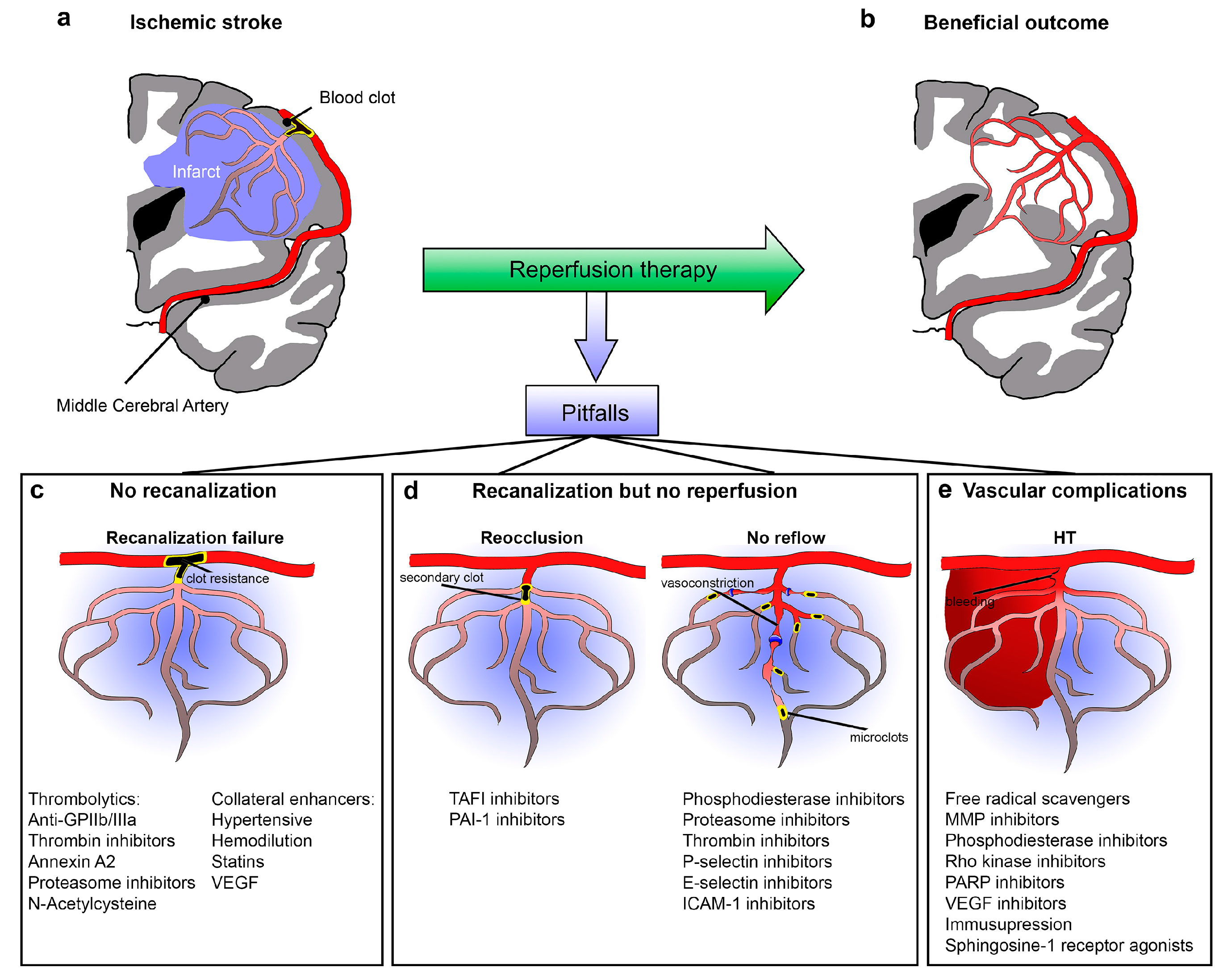
Ijms Free Full Text Improving Cerebral Blood Flow After Arterial Recanalization A Novel Therapeutic Strategy In Stroke Html

Distal Versus Proximal Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Different Mechanisms Semantic Scholar

The Experimental Protocol And Timeline For The Middle Cerebral Artery Download Scientific Diagram
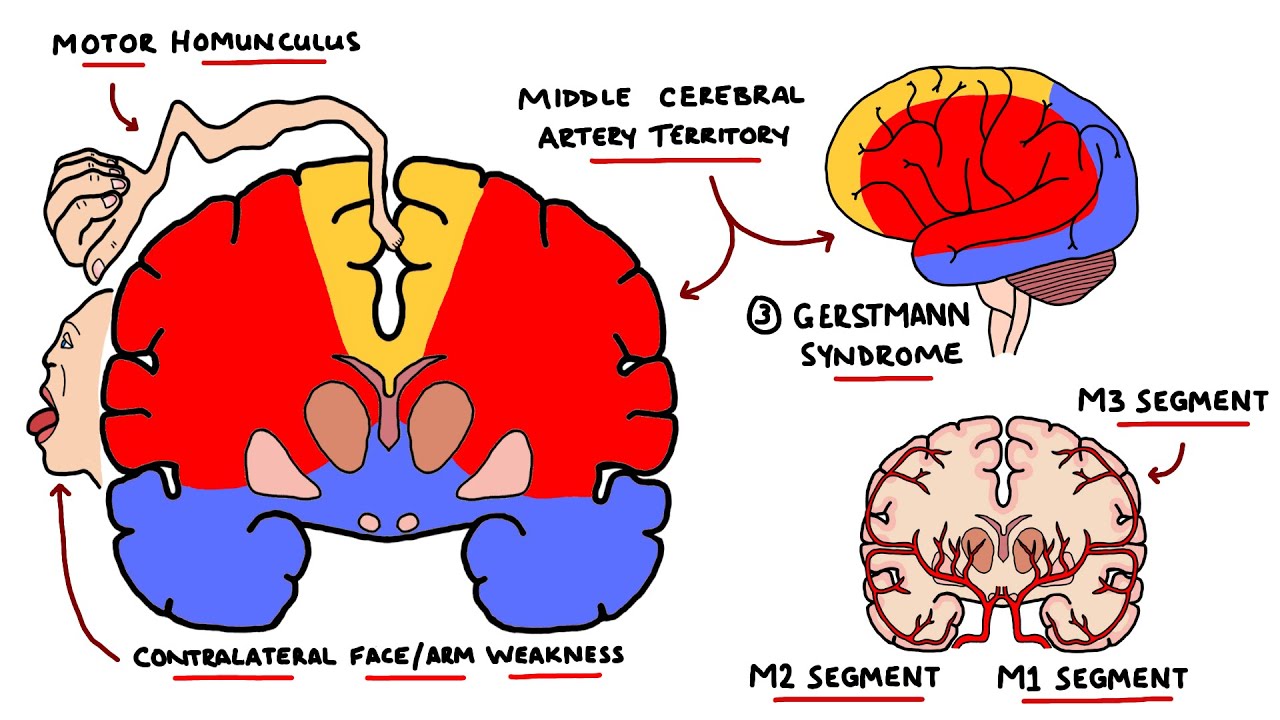
Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke Syndromes Mca Stroke Syndromes With Gerstmann Syndrome Lesions Youtube

Symptoms And Signs Of Basilar Artery Occlusion Download Table

Major Human Arteries And Specific Clinical Symptoms Produced After Stroke Download Scientific Diagram

Anterior Cerebral Artery Stroke Syndrome Aca Stroke Syndrome Stroke Syndromes Youtube

Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke Youtube
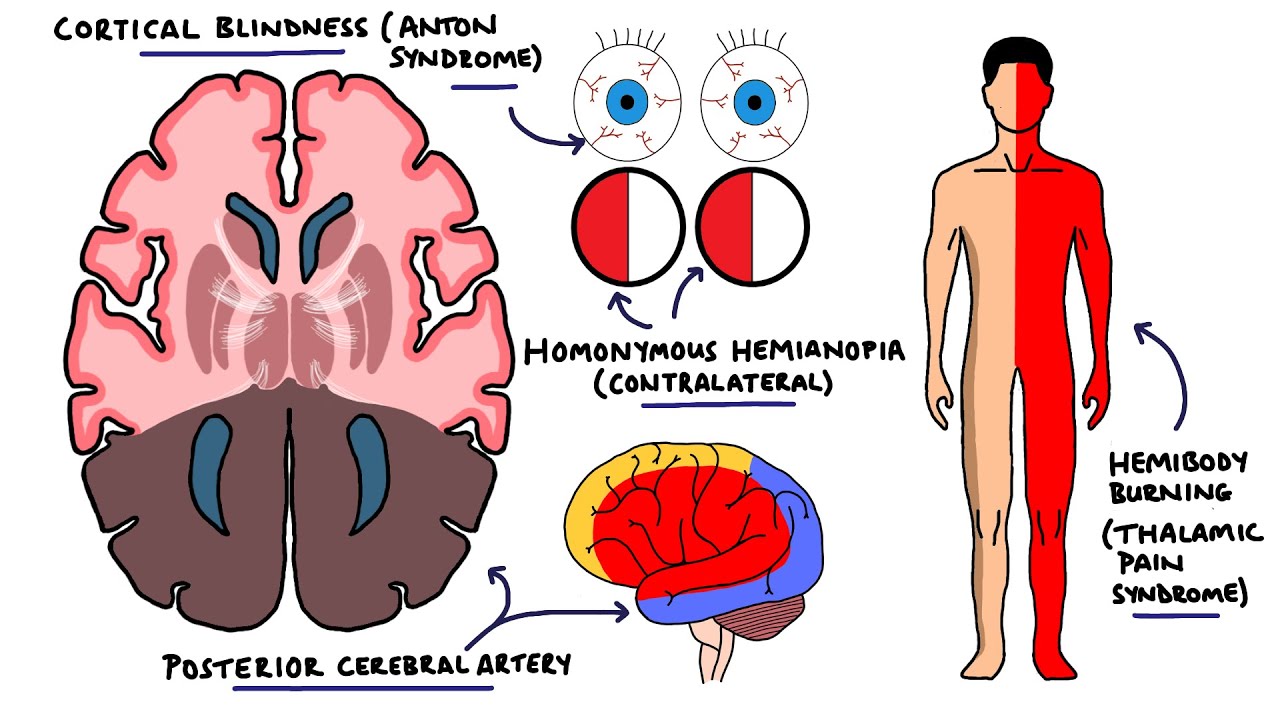
Anterior Cerebral Artery Stroke Syndrome Aca Stroke Syndrome Stroke Syndromes Youtube

Pdf Pathophysiology Of Acute Ischemic Stroke Semantic Scholar
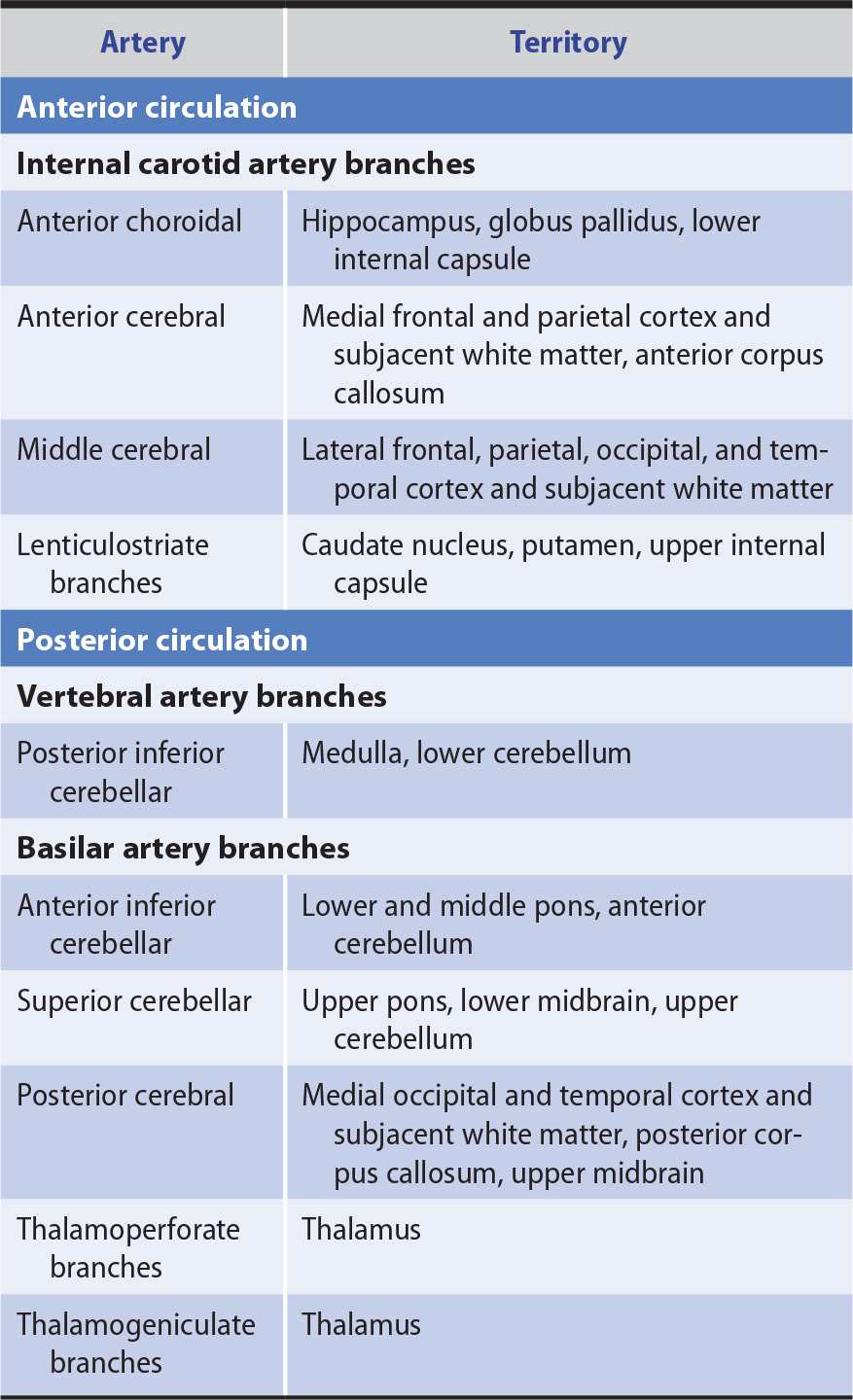

Posting Komentar untuk "Cerebral Artery Occlusion Pathophysiology"