Icp Levels Severe Head Injury
There is no high-quality evidence that monitoring and treating ICP is beneficial. In contrast to most other organs the brain is protected by a stiff skull.

Brain Surgery Severe Head Injury With Surgical Craniotomy Medical Exhibit Brain Surgery Subdural Hematoma Brain Surgery Recovery
Sustained increases to 20 mm Hg for 5 min may need treatment34 Though the efficacy of treatment based.

Icp levels severe head injury. A defined strategy for volume replacement and fluid balance that includes maintenance of normovolemia and colloid osmotic pressure in combination with a neutral to a slightly negative fluid balance is a cornerstone of the intracranial pressure ICP- targeted therapy for severe TBI. The purpose of this study was therefore to measure dialysate potassium in severely head injured patients and to correlate these results with measurements of intracranial pressure ICP patient outcome and levels of dialysate glutamate and lactate and cerebral blood flow CBF to determine the role of ischemia in this posttraumatic ion dysfunction. Hyperventilation is recommended as a temporizing measure for the reduction of elevated ICP. 50 While brief episodes of. Raised ICP is an important secondary insult in brain-injured patients and a predictor of poor outcome after traumatic brain injury. Which action by the nurse is appropriate.
None Level II. We obtained data from 14 neurotrauma ICUs in Europe. When ICP is greater than 40mmHg there is almost always some neurological dysfunction impairment of consciousness problems breathing pupil dilation compression of brain found on MRI as well as impairment of the brains electrical activity an abnormal EEG. C ICP monitoring is appropriate in patients with severe head injury GCS between 3 and 8 after cardiopulmonary resus- citation and an abnormal computed tomographic CT. ICP is a valuable indicator of injury severity after TBI and there is a well-described relationship between intracranial hypertension although the definition of this varies and mortality after sTBI. TBI Guidelines Brain Trauma Foundation 2007 Level I.
The purpose of this study was therefore to measure dialysate potassium in severely head injured patients and to correlate these results with intracranial pressure ICP outcome and also with the levels of dialysate glutamate lactate and cerebral blood flow CBF so as to determine the role of ischemia in this posttraumatic ionic dysfunction. The Brain Trauma Foundation BTF recently updated recommendations for intracranial pressure ICP monitoring in severe traumatic brain injury TBI. In traumatic brain injury TBI patients desmopressin administration may induce rapid decreases in serum sodium and increase intracranial pressure ICP. During traumatic brain injury intracranial hypertension ICH can become a life-threatening condition if it is not managed quickly and adequately. In one prospective RCT of patients with traumatic brain injury ICP measurement didnt affect outcomes. Conventional therapy failed to control elevated ICP in 36 of TPN patients and 38 of EN patients.
Of these patients subsequent barbiturate therapy failed to control ICP in 56 of TPN patients and 64 of EN patients. Severe TBI GCS 8 after resuscitation with abnormal CT brain hematomas contusions swelling herniation or compressed basal cisterns. In an international multi-centre study we aimed to report changes in serum sodium and ICP after desmopressin administration in TBI patients. Prophylactic hyperventilation PaCO2 of 25 mmHg or less is not recommended. Increased ICP is an important cause of secondary brain injury in TBI and both degree and duration of high ICP is associated with poor outcomes. Changes were not statistically significant in either group.
Hyperventilation should be avoided during the first 24 hrs after. Intracranial pressure ICP monitoring Licox or Jugular venous brain oxygen monitoring will be done in all salvageable patients with the following conditions. The effect of ICP monitoring on outcomes is controversial and compliance with BTF guidelines is variable. Physicians use therapeutic hyperventilation to reduce elevated intracranial pressure ICP by manipulating autoregulatory functions connected to cerebrovascular CO 2 reactivity. Intracranial pressure ICP is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid CSF inside the skull and on the brain tissue. In a study of patients with head trauma 54 of patients had increased ICP but only 35 had papilledema on fundoscopic examination 18.
Intracranial pressure ICP and cerebral perfusion pressure CPP are frequently monitored in severely head injured patients. The benefit of ICP monitoring may be greater in certain disease states eg traumatic brain injury as compared to others eg ischemic stroke. The purpose of this study was to assess both compliance and outcomes at level I trauma centers. In contrast to hemorrhage and hemorrhagic shock possibilities for life-saving interventions are. 8 50 54 This relationship becomes proportionally greater as the value of ICP increases with a sixfold increase risk of death when ICP is greater than 40 mmHg. Patients in group 2 also had decreased mean ICP values -120 mm Hg and increased mean CPP values 22105 mm Hg.
To establish which one ICP or CPP is more predictive of outcome and to examine whether there are significant threshold levels in the determination of outcome receiveroperating characteristic ROC curves were used to. Papilledema is a reliable sign of intracranial hypertension but is uncommon after head injury even in patients with documented elevated ICP. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury and at rest is normally 715 mmHg for a supine adultThe body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in. Intracranial pressure was greater than 20 mm Hg in 75 of TPN patients and 73 of EN patients. A patient with a head injury has an arterial blood pressure is 9250 mm Hg and an intracranial pressure of 18 mm Hg. According to the present limited study pedal pump and thoracic pump techniques may be used safely in patients with severe brain injuries.
An increase in ICP may therefore impede cerebral blood flow CBF and cause ischaemia.
Guidelines For The Management Of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury 2020 Update Of The Decompressive Craniectomy Recommendations Spine Section

Cushing S Triad What Is It Causes Assessment Findings Treatment And More Osmosis

Secondary Brain Injury Sbi Pathophysiology Nurse Your Own Way Nurse Nursing Education Pediatric Nursing

Increased Intracranial Pressure Icp Nursing School Studying Emergency Nursing Medical School Studying

Pin On Neuro Medical Surgical Nursing School Brain Sheets Study Sheets

Brain Injury Types Levels Save Your Head Brain Injury Brain Injury Awareness Traumatic Brain Injury

Elevated Intracranial Pressure Icp Emcrit Project
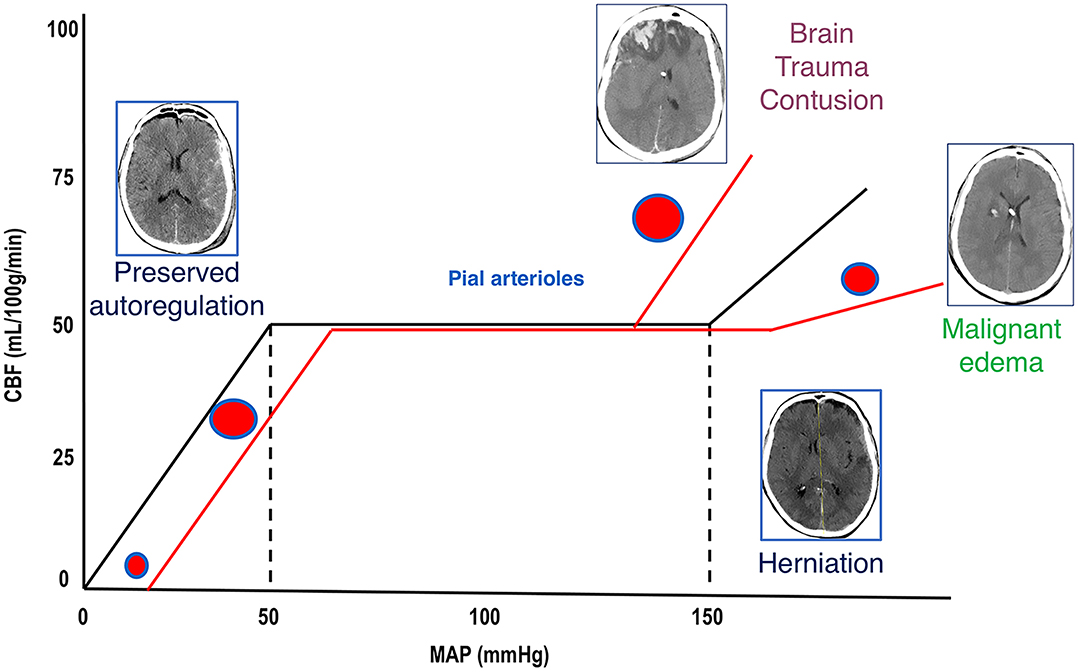
Frontiers Escalate And De Escalate Therapies For Intracranial Pressure Control In Traumatic Brain Injury Neurology
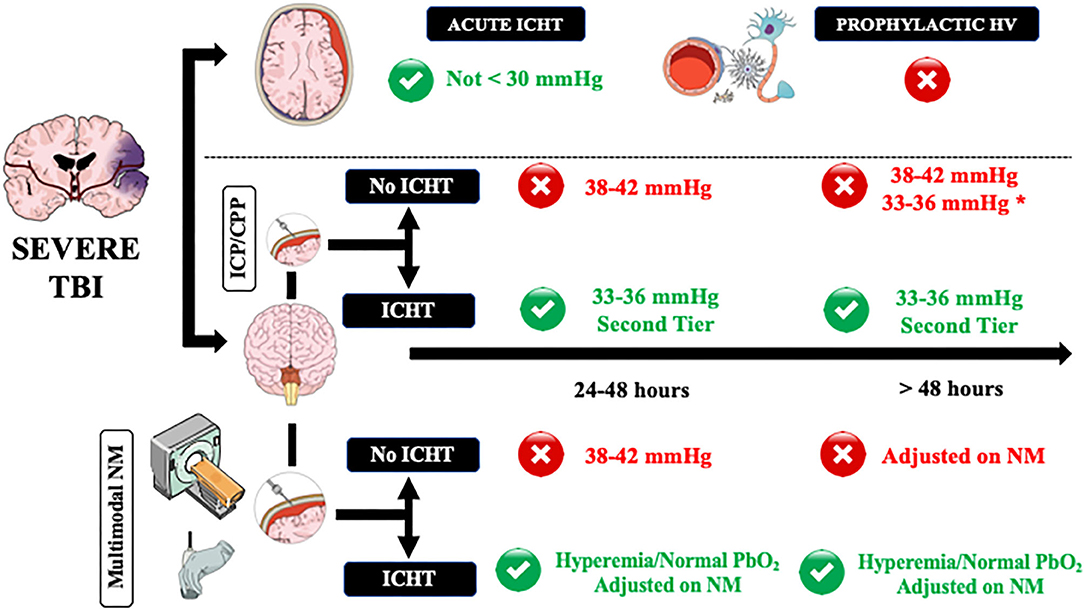
Frontiers Hyperventilation In Adult Tbi Patients How To Approach It Neurology

Even Artichokes Have Hearts Nurse Nursing Mnemonics Intracranial Pressure

Collaborative Care For Increased Intracranial Pressure Intracranial Pressure Nursing School Notes Icu Nursing



Posting Komentar untuk "Icp Levels Severe Head Injury"