Visual Field False Positive
Fixation losses 33 false-negative rate 20 and false-positive rate 20 1724 25 2627. 321 Visual Field Testing at Bedside Bedside visual field testing is quick and easy but has relatively poor reliability depending on the patients ability to identify and describe the visual field defect.

Advances In Visual Field Testing For Glaucoma Management
The reliability criteria for VF selection were as follows.

Visual field false positive. False-positive errors identify trigger happy patients who respond in the absence of light stimulus. Assessment of false positives with the Humphrey Field Analyzer II. Visual field testing is a vital component in the diagnosis and follow-up of. Tests approximately 24 points in all 4 quadrant. Fixation losses as well as false positives and negatives should typically be less than 20 to 30 for the test to be considered clinically valuable see the discussion below. 11 charts had false positive errors on both eyes and the records indicate that these patients misunderstood the testing instructions.
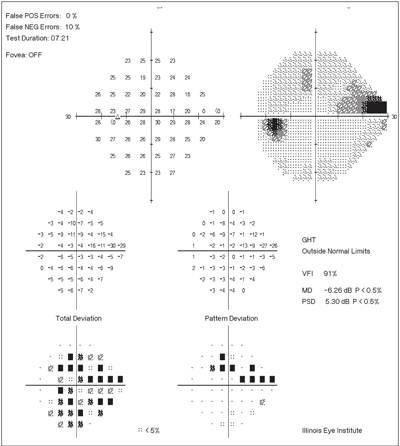
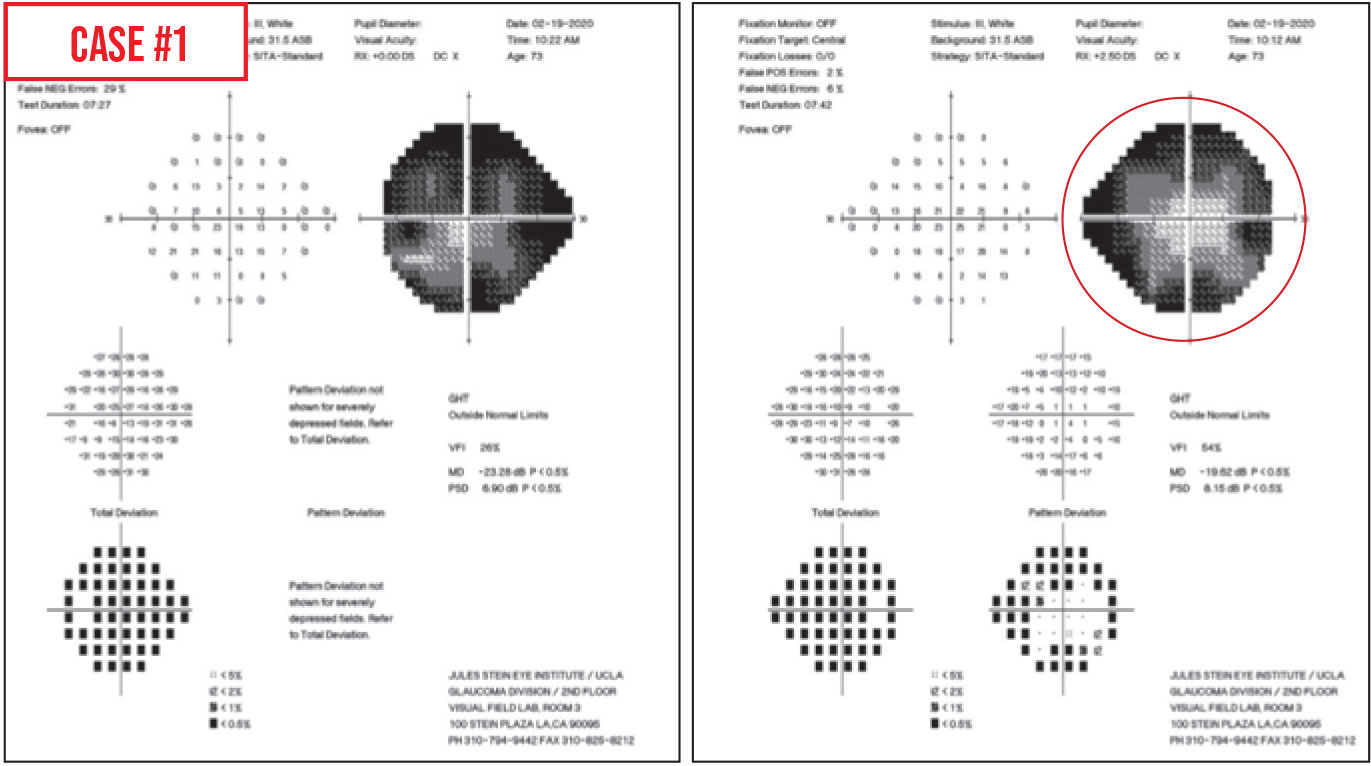
Tests for false positives and false negatives. False positive rates greater than 20 suggest an unreliable test that can mask or minimize an actual scotoma and can in extreme cases result in a visual field with impossibly high threshold values. As a result the visual field appears better than the true visual field of the patient which is shown on the right. False positive and False negative 33 These cut-offs were based on statistical significance not clinical significance For false positives as little as 5-10 may destroy the credibility of the field 6 Steps in Analyzing Visual Field Patient Performance Take time to set patient up properly Patient comfortable. The top visual field contains characteristic white scotomata which represent areas of impossibly high retinal sensitivity. Reliability criteria were established as less than 20 fixation losses less than 33 false-negative error and less than 33 false-positive error as.
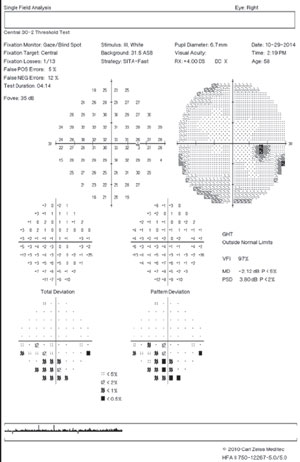
9 rows Of the three reliability indices false positives are the least variable in testretest studies. VISUAL FIELD INDICES VFI MD and PSD Three summary indices of visual fi eld statusVFI MD and PSDappear on the SFA printout. If more than one. Customizable stimulus and background. In such cases they gray scale may look. Visual fields should be tested monocularly given that the overlap in binocular fields may mask visual field defects.
138 1st test 2nd test. Testing time typically under 5 minutes in experienced test takers is also given. Patient reliability in Humphrey automated visual field testing was studied in 106 randomly selected chronic open-angle glaucoma patient charts which provided 768 tests mean 72 - 48 fields. The field on the left is unreliable because the patient responded in the absence of a stimulus. Wide field of view tested 30 degrees from fixation horizontally and 24 degrees vertically. If this index is higher than 15 the test needs to be invalidated or repeated even 5 to 10 should be scrutinizedTests with high false positives are automatically removed from a Humphrey.
Tests on both sides of main meridians. VFI Visual Field Index is a staging index designed to be less affected by cataract and also to provide improved correspondence to ganglion cell loss compared to MD. They are calibrated according to the patients overall responses therefore detecting when responses occur too soon after presenting a stimulus is. False positives are primarily important in tests that have defectsthey are not a reason to invalidate an otherwise unremarkable or clear visual field test. High FP error frequencies can have adverse effects on MD and PSD leading clinicians and researchers to an inaccurate determination of the amount and severity of visual field loss. Upon return visit 3 weeks later the patient was carefully instructed to respond only when she saw the light resulting in the bottom visual field which shows good reliability and demonstrates the patients dense superior visual field.
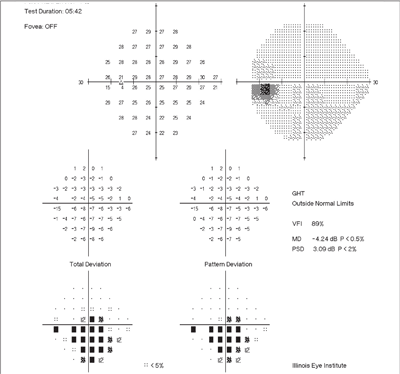
Of the charts audited 56 were found to show false-positive screening errors during the first FDT test sequence for a 192 false positive rate -445 sampling error. The N-30-1 test can be used for screening a large number of subjects in the general public seeing that the incidence of disease is expected to be low false positives are preferably kept to a minimum and many visual field defects due to several disorders including those located in the nasal periphery can be detected with this rapid method. FIGURE 8-7 The example above shows the impact of a high rate of false positive answers on the visual field. VFI is approximately 100 in. A false-positive rate of 15 compromises test results4. Fast visual field testing approximately 3 minutes per eye.
Tests blind-spot position.
Sharpen Your Visual Field Interpretation Skills

08 Hfa Reliability Indices Subjects To Cover 01 Definitions And Concepts 02 Types Of Perimetry 03 Sources Of Error In Perimetry 04 Humphrey Field Analyzer Hfa 05 Hfa Testing Patterns 06 Hfa Testing Strategies 07 Hfa Displays 08 Hfa
High False Positive Rate Visual Field American Academy Of Ophthalmology
How To Interpret Visual Fields 5 Most Common Patterns Eyeguru
10 Tips For Improving Visual Fields

Ophthalmic Professional Avoiding Fixation Losses In Visual Fields Testing
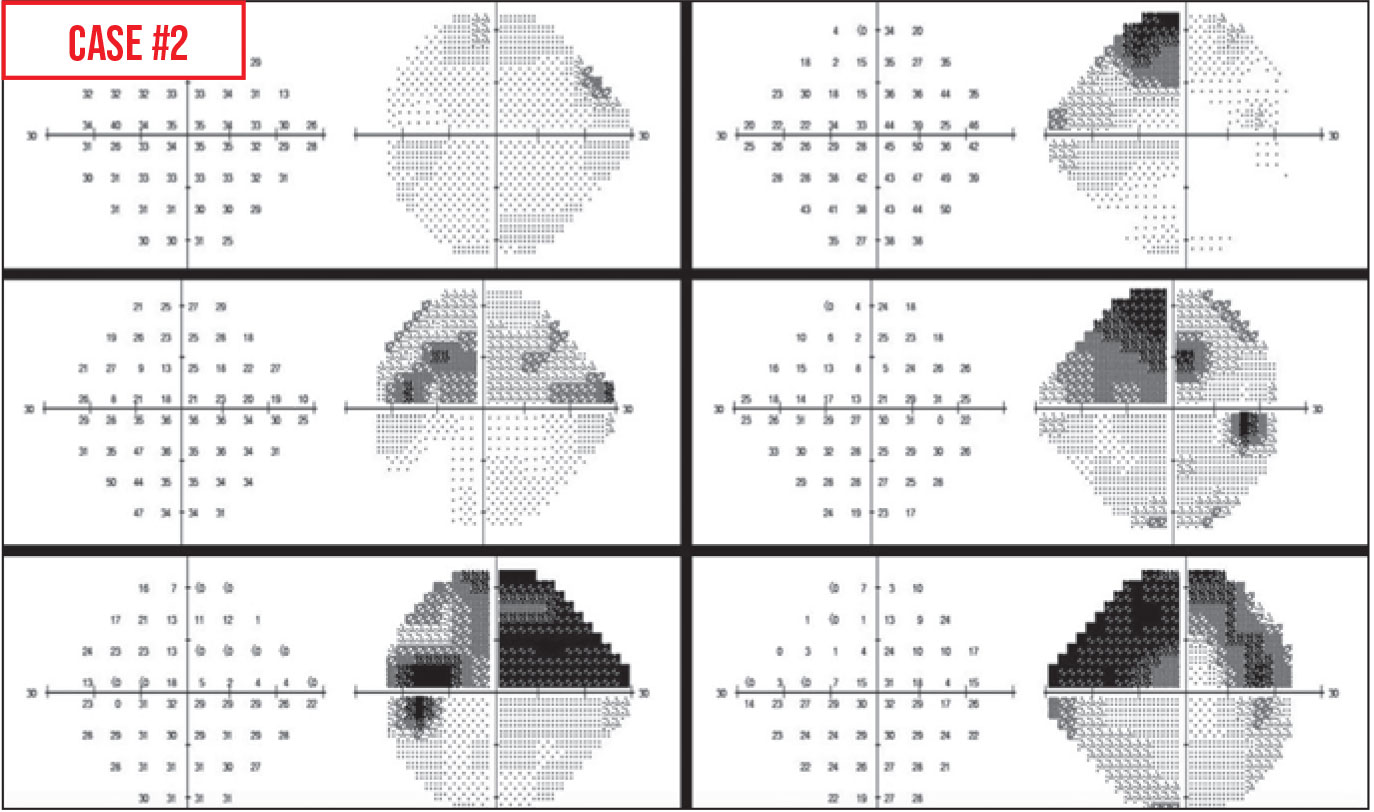
Recognizing Artifacts In Visual Field Testing
Recognizing Artifacts In Visual Field Testing

How To Interpret Visual Fields 5 Most Common Patterns Eyeguru

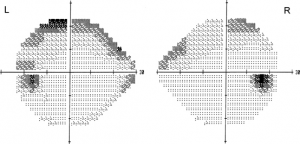
Visual Field By 24 2 Humphrey Automated Perimetry At Presentation Download Scientific Diagram
Sharpen Your Visual Field Interpretation Skills

Ophthalmic Professional Avoiding Fixation Losses In Visual Fields Testing

08 Hfa Reliability Indices Subjects To Cover 01 Definitions And Concepts 02 Types Of Perimetry 03 Sources Of Error In Perimetry 04 Humphrey Field Analyzer Hfa 05 Hfa Testing Patterns 06 Hfa Testing Strategies 07 Hfa Displays 08 Hfa

Posting Komentar untuk "Visual Field False Positive"